[OS] Mutual Exclusion
1. Mutual Exclusion(상호 배제)
1.1. 원칙(목표)
- 임계영역에는 오직 한 개의 프로세스/스레드만 진입하게 하는 것
- 입구에 게이트를 두고, 이를 잠글 수 있는 열쇠 ‘Lock’을 만드는 것
- Lock이 on이 되어있으면 못 들어가게 함
1.2. Mutual Exclusion primitives
enterCS()- 임계 영역 진입 전 검사하는 것
- 다른 프로세스가 임계 영역 안에 있는 지 검사
exitCS()- 임계 영역을 벗어날 때 후처리
- 다른 프로세스가 임계 영역을 떠났음을 알림
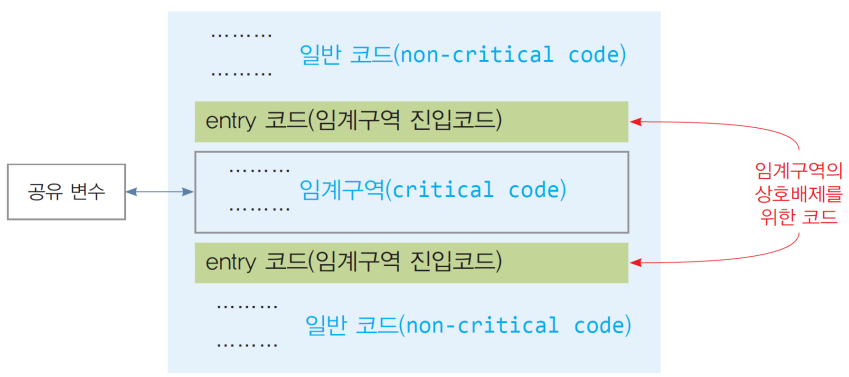
1.3. 상호 배제를 포함하는 프로그램
- 일반 코드(non-critical code)
- 공유 데이터를 액세스하지 않는 코드
- 임계구역 진입 코드(entry code)
- 상호배제를 위해 필요한 코드 (enterCS())
- 임계구역에 진입하기 전 필요한 코드 블록 - 현재 임계구역을 실행 중인 스레드가 있는지 검사
- 없다면, 다른 스레드가 들어오지 못하도록 조치
- 있다면, 진입이 가능해질 때까지 대기
임계구역 코드(critical code)
- 임계구역 진출 코드(exit code)
- 상호배제를 위해 필요한 코드 (exitCS())
- 임계구역의 실행을 마칠 때 실행되어야 하는 코드 블록 - entry code에서 대기중인 스레드가 임계구역에 진입할 수 있도록 entry code에서 취한 조치를 해제하는 코드
1.4. 구현 주의사항
- 상호 배제를 구현 시 아래의 조건들을 만족해야 함
- 하지만 쉽지만은 않은 작업
- 상호 배제 (mutual exclusion)
- 한 프로세스가 임계구역에 들어가면 다른 프로세스는 임계구역에 들어갈 수 없는 것
- 한정 대기 (bounded waiting)
- 어떤 프로세스도 무한 대기하지 않아야 함
- 진행의 융통성 (progress flexibility)
- 한 프로세스가 다른 프로세스의 진행을 방해해서는 안 된다는 것
1.5. 상호 배제 구현 방법
- 소프트웨어적 방법
- 두개의 프로세스에 대해…: 데커(Dekker) 알고리즘, 피터슨(Peterson) 알고리즘 등
- 여러 프로세스에 대해…: Lamport의 빵집 알고리즘 등
- 하드웨어적 방법 → 오늘날에는 대부분 하드웨어 기반 동작
- 임계 구역 진입/진출 코드에 구현
- 방법 1) 인터럽트 서비스 금지
- 방법 2) 원자 명령(atomic instruction) 사용
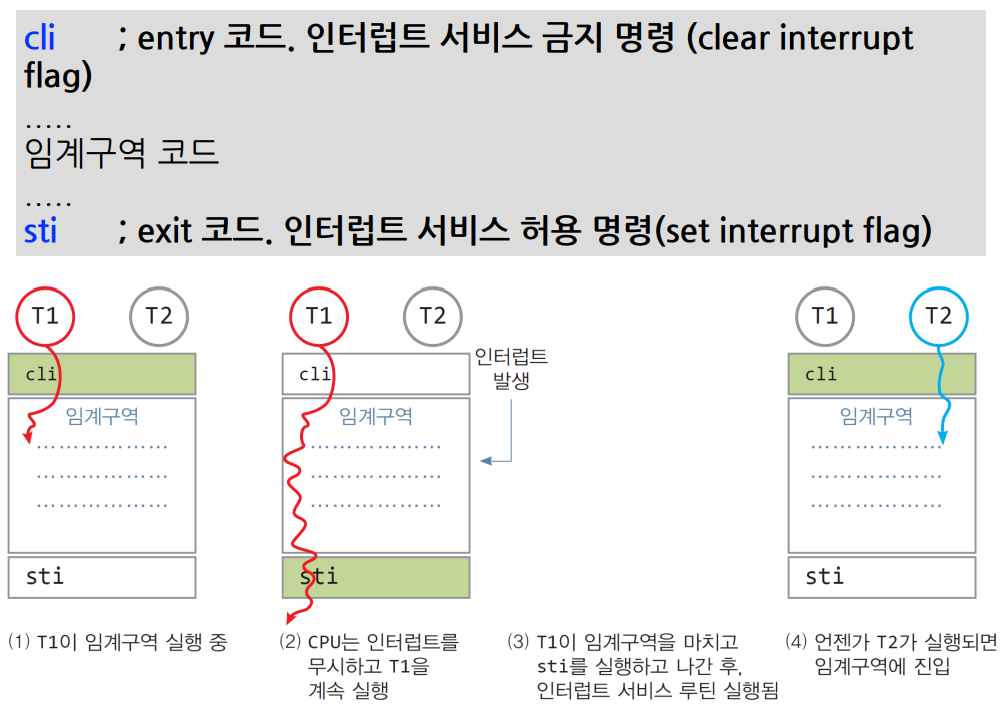
2. Mutex 구현: 인터럽트 서비스 금지
- 임계구역 entry 코드에서 인터럽트 서비스를 금지하는 명령 실행
- 장치로부터 인터럽트가 발생해도 CPU가 인터럽트를 무시함. 즉, 인터럽트 루틴을 실행하지 않음
- 인터럽트를 금지한다 → Scheduling에 의한 context switching도 자연스럽게 금지됨.
- 스레드도 중단되지 않음
- 장치로부터 인터럽트가 발생해도 CPU가 인터럽트를 무시함. 즉, 인터럽트 루틴을 실행하지 않음
- cil: clear interrupt
- stl: set interrupt
2.1. 문제점
- 모든 인터럽트가 무시되는 문제
- 시스템의 효율적인 운영을 방해하기 쉬움
- 멀티코어 CPU 또는 다중 CPU에서는 활용이 불가능
- 모든 CPU의 인터럽트가 멈춤
- 진행의 융통성 조건 불충족
2.2. 해결책
- Lock을 현재 엑세스하고 있는 메모리에만 국한시켜야 함
2.3. 주의사항
- Lock을 단순하게 on/off가 되어서는 안 됨
- 문이 열려있는지 닫혀있는지 확인하기 위한 Lock도 공유 데이터
- 공유자원 동기화 이슈가 발생함
- 문이 열려있는지 닫혀있는지 확인하기 위한 Lock도 공유 데이터
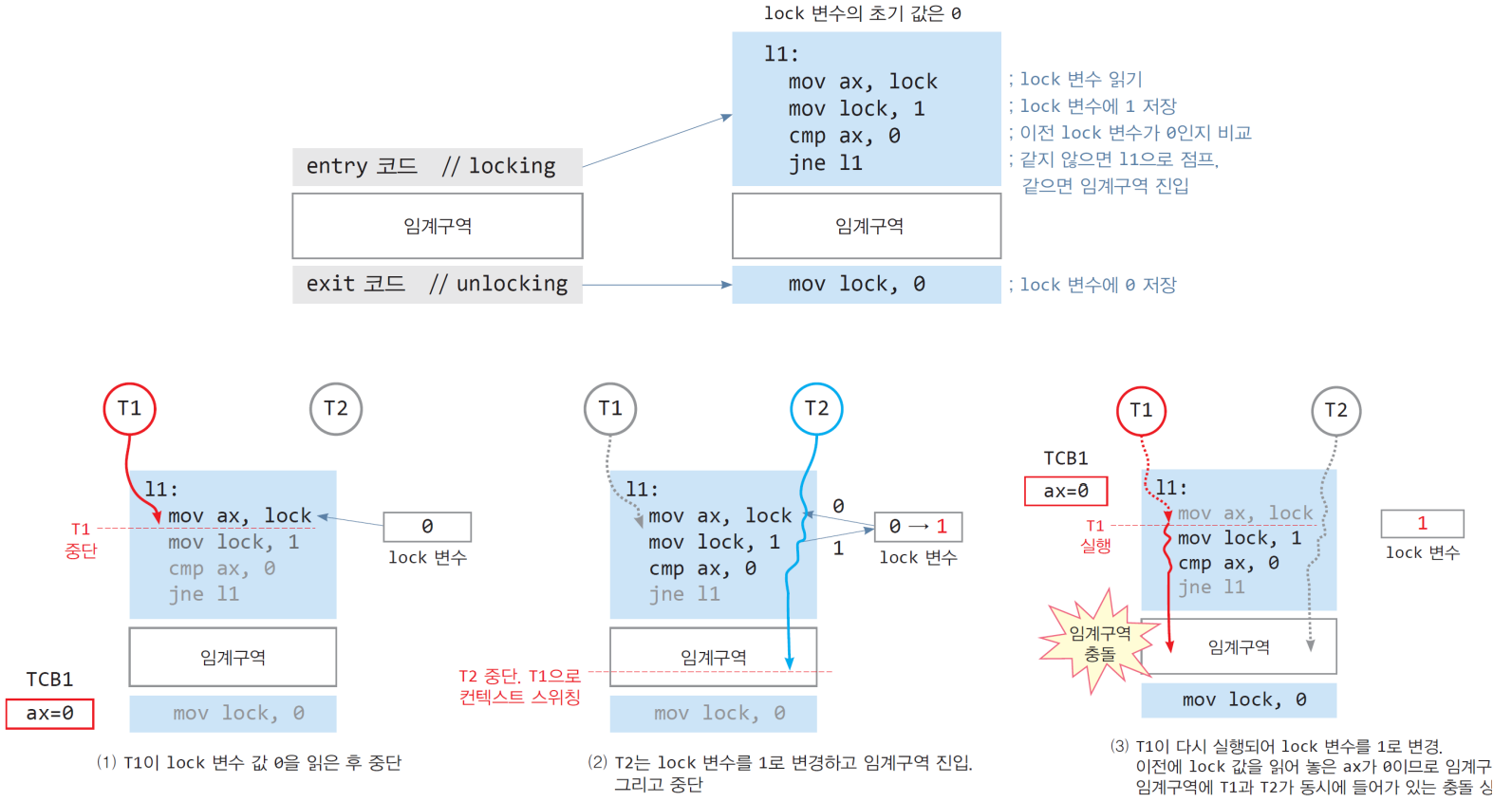
2.4. lock이 부실한 예시
- 문제점: 상호배제 조건 불충족
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
const int count = 200000;
int sum = 0; // global variable, shared data
bool lock = false; // lock
void* myThread1(void *p) {
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
while(lock == true); // critical section
lock = true;
sum += 1;
lock = false;
}
return 0;
}
void* myThread2(void *p) {
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
while(lock == true); // critical section
lock = true;
sum -= 1;
lock = false;
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
pthread_t tid1, tid2; // thread id
int count = 200000;
int *ret1, *ret2;
printf("Start!\n");
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, myThread1, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, myThread2, NULL);
pthread_join(tid1, (void**)&ret1); // waiting for 'tid1'
pthread_join(tid2, (void**)&ret2); // waiting for 'tid2'
printf("sum = %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
2.5. 해결한 예시(?)
- 서로의 상태까지 확인이 가능하도록 만들어줌
- 문제점: 한정대기 조건 불충족
- 무한루프에 빠지기 쉽다!
- ex: lock1이 true가 된 상태에서 컨텍스트 스위칭 발생하고, lock2가 true가 되고 다시 컨텍스트 스위칭 발생하면 둘다 while에서 대기해야 함
- 무한루프에 빠지기 쉽다!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
const int count = 200000;
int sum = 0; // global variable, shared data
bool lock = false; // lock
void* myThread1(void *p) {
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
while(lock == true); // critical section
lock = true;
sum += 1;
lock = false;
}
return 0;
}
void* myThread2(void *p) {
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
while(lock == true); // critical section
lock = true;
sum -= 1;
lock = false;
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
pthread_t tid1, tid2; // thread id
int count = 200000;
int *ret1, *ret2;
printf("Start!\n");
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, myThread1, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, myThread2, NULL);
pthread_join(tid1, (void**)&ret1); // waiting for 'tid1'
pthread_join(tid2, (void**)&ret2); // waiting for 'tid2'
printf("sum = %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
2.6. 진짜 해결한 예시
- 서로 사용권 자체를 주고받기
- 진행의 융통성은 여전히 부족
- 자원은 비어있는데 사용을 못하는 문제 발생
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
const int count = 200000;
int sum = 0; // global variable, shared data
int lock = 1; // lock
void* myThread1(void *p) {
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
while(lock == 2); // critical section
sum += 1;
lock = 2;
}
return 0;
}
void* myThread2(void *p) {
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
while(lock == 1); // critical section
sum -= 1;
lock = 1;
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
pthread_t tid1, tid2; // thread id
int count = 200000;
int *ret1, *ret2;
printf("Start!\n");
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, myThread1, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, myThread2, NULL);
pthread_join(tid1, (void**)&ret1); // waiting for 'tid1'
pthread_join(tid2, (void**)&ret2); // waiting for 'tid2'
printf("sum = %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
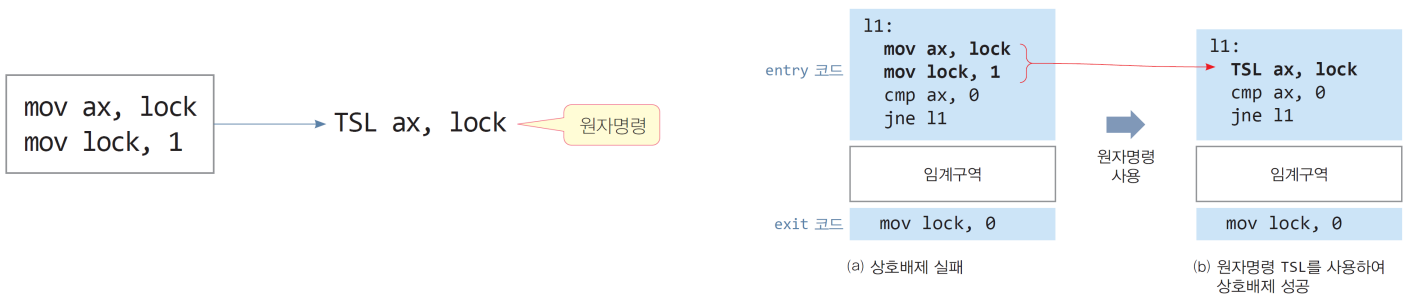
3. Mutex 구현: 원자 명령(atomic instruction)
- lock 변수를 이용한 상호배제 실패 원인? entry 코드에 있음
- lock 변수 값 읽는 명령과 lock 변수에 1 저장하는 2개의 명령 사이에 컨텍스트 스위칭 될 때 문제 발생
3.1. 해결책: 원자 명령(atomic instuction) 도입
- lock을 읽어들이는 명령, lock 변수에 1을 저장하는 2개의 명령을 처리하는 동안 컨텍스트 스위칭 없이 한번에 처리하는 명령어가 필요
- 원자 명령 어셈블리 코드: TSL(Test and Set Lock)
- 하드웨어의 지원이 필요
3.2. 예시: Test and Set
- 하드웨어의 지원을 받은 Lock을 구현한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdatomic.h> //필요함
const int count = 200000;
int sum = 0; // global variable, shared data
//bool lock = false; // lock
atomic_flag lock = ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT;
void* myThread1(void *p) {
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
while( atomic_flag_test_and_set(&lock) );
sum += 1;
atomic_flag_clear(&lock);
}
return 0;
}
void* myThread2(void *p) {
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
while( atomic_flag_test_and_set(&lock) );
sum -= 1;
atomic_flag_clear(&lock);
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
pthread_t tid1, tid2; // thread id
int count = 200000;
int *ret1, *ret2;
printf("Start!\n");
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, myThread1, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, myThread2, NULL);
pthread_join(tid1, (void**)&ret1); // waiting for 'tid1'
pthread_join(tid2, (void**)&ret2); // waiting for 'tid2'
printf("sum = %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
이 포스팅은 작성자의 CC BY-NC 4.0 라이선스를 준수합니다.